Are you recycling your milk cartons and juice boxes properly? In this article, you will find everything you need to know.
One type of household packaging that still creates confusion when it comes to recycling is multilayer packaging. This type of packaging includes Tetra Paks, Tetra Bricks, liquid paperboard, long-life containers, milk or juice cartons or boxes, or soup containers. Here you will learn how easy it is to recycle your milk cartons and juice boxes. All you have to do is make sure your local authority accepts them.

Quick Navigation
What is Multilayer Packaging?
It is a type of packaging made using multiple layers of different materials. The materials usually include paper or cardboard, different plastics, and in some cases aluminum.
Combining these different materials gives several benefits. Multilayer packaging containers have protective properties that provide storage stability of food items. They offer a longer shelf life for food products. Also, they are easy to handle and cheaper to transport thanks to their thin and lightweight structure.
Multilayer packaging can be made with up to 11 different layers. This means that recycling multilayer packaging materials can be tricky as it requires the separation of the different layers.
The good news is that recycling processes and the availability of suitable facilities are improving, and so recycling rates are also increasing. Always check with your local authority to see if they accept cartons or Tetra Paks.

Common Household Examples
Multilayer packaging is used to store many different products in various industries. The following food items are stored in multilayer cartons :
- Standard milk
- Long-life (UHT) milk
- Flavored milk
- Fruit juice
- Syrups
- Stock cartons
- Soups
- Custard


What Are They Made From?
There are many types of multilayer packaging materials used for cartons and other food storage. The most common types of containers are gable-top cartons and aseptic bricks.
- Gable-top cartons store fruit juices and milk. They are generally made with paperboard sandwiched between two layers of plastic.
- Aseptic brick-shaped cartons are made from five layers and include a layer of aluminum foil. Products stored in aseptic cartons do not need refrigeration until opened. An example is a long-life (or UHT) milk carton. These can also be used to protect medications from bacteria.
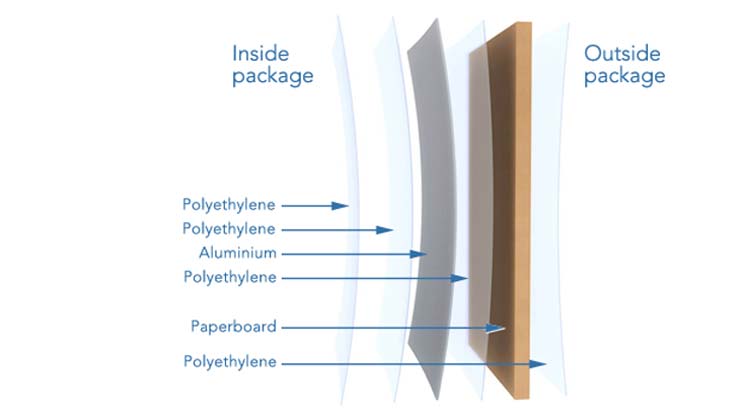
Tetra Pak’s are a typical example of multilayer packaging. Tetra Paks are aseptic cartons that use six layers of material. Paperboard is the thickest layer, making up 75% of the package. Multiple layers of plastic account for a further 20% and the remaining 5% is a single layer of aluminum. Bonding the layers together using heat and pressure forms the multilayered material.
Why Are They Used?
By combining the different materials into multilayer packaging, you get the benefits of all the different layers. They include:
- PROTECTIVE LAYERS – Tetra Pak’s protect the contents from light, oxygen, air, dirt, and moisture. All of these can degrade the food contained in the packaging.
- LONG LIFE – The protective properties of Tetra Pak’s layered packaging keeps the contents fresh for a long time reducing food wastage. It also does not need to be refrigerated until opened, increasing the shelf life of the product.
- LIGHTWEIGHT – Another benefit of Tetra Pak’s and other similar packaging is that they do not weigh much. This means easier handling and a reduction in energy use during transportation.
An excellent example of where this can be of great benefit is in the Indian market. Temperatures across India can range from sub-zero to over 50 degrees Celsius and relative humidities up to 100%. These variations result in complex issues in the supply chain. Multilayer packaging can protect the products from moisture and other elements when transported through the country. Overall it can improve food security and increase product stability and shelf life.
Can They Be Recycled?
Yes, it is possible to recycle multilayer packaging.
However, as with many items reported as recyclable, it is not an easy process. The mechanical recycling process used by many material recovery facilities (MRF’s) struggles with these multilayer materials. The process depends on local facilities having the capability to separate these types of materials first and the availability of processing plants.
There are two ways to recycle multilayer packages:
- With their high paper content, paper mills can process them. The paper fibers are extracted and used to make new paper products like tissues and office paper. The plastic and aluminum are used to make ceiling tiles, wallboard or as energy to fuel the mill.
- Cartons are transformed into construction boards. The materials are not separated; instead, they are shredded and pressed back together into large sheets.
Watch this great video on the recycling of cartons.
How to Recycle Milk Cartons
Here are some simple steps on how to recycle milk cartons, juice cartons, or other liquid paperboard cartons:
- Check if your local facility or recycling services accept multilayer cartons. See links below.
- Make sure the carton is empty of its contents. Rinse if necessary, and let it dry.
- Read the rules from your local council as some areas recommend you flatten the carton while others do not require this.
- You may also be able to put the lid back on.
- Place the item in your recycling bin.
Please be sure to check with your local authority to make sure they do accept multilayer cartons. See the links below to find out if your local authority does and to check the rules.
| United States | Recycling Cartons |
| United Kingdom | How to recycle drink cartons |
| Australia | Most councils in Australia collect these cartons. However check with your local council to be sure. |
| New Zealand | Check with your council. Some programs were introduced late in 2019 to recycle UHT milk and juice cartons. |
| Canada | How to recycle cartons |
If you cannot find the information in the links, you can always try the Tetra Pak website. You can find recycling information links for each country on their website. Go to their main page and select your country in the top right-hand corner then go to Sustainability/Local Pages and view their information.

What Are Some Alternatives?
In the new era of Covid-19, many of us are stocking up on long-life consumables more than usual. I know I have a hidden stash of long-life milk just in case something changes again. But there are also alternatives to increasing your stock supplies. There are simple changes we can make to reduce our reliance on multilayer cartons. Here are some examples:
- Make your own stock or soups rather than buying packaged items.
- Make your own juices from scratch.
- Buy glass containers where possible as they can be reused or recycled into new products.
- Buy products contained in more easily recyclable plastic like the plastic numbers 1, 2, 4 or 5.
Wrap Up
These complex mixed materials used to store our milk and juices are a tricky lot. There are real benefits to using this type of packaging in a world where food waste is a massive issue. They provide protection and longevity to products while reducing energy use and delivery impacts. At the same time, the complexity of the materials can lead to poor recycling outcomes. For example, materials are downcycled instead of recycled.
So, what can we do. Well, we can reduce as much as possible and recycle milk cartons and juice cartons through our local recycling service if available.
Are you looking for more ways to help protect our environment?
If you want to learn about other hard to recycle or confusing items, check out our articles on egg cartons, shredded paper or pringle cans.
Sources
- Tetra Pak main web page Sustainability topic
- BASF, 2019, Multilayer packaging: innovative and sustainable
- Recycle Cartons website
- Doyle, Amande, 2018, New technique for recycling multi-layer packaging, TheChemicalEngineer.com
- Wallentin, 2017, Multi-layer materials, Packagingsense.com
- 2017, What Is Aseptic Packaging?, eagleflexible.com














